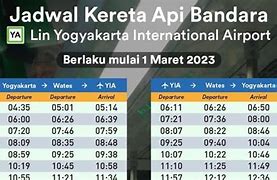
Admin Processing Bfi Finance Adalah
Peralatan Bersih-Bersih
Selain barang elektronik, peralatan bersih-bersih pun tidak kalah pentingnya! Dengan memberikan kado pernikahan ini secara tidak langsung Anda dapat meringankan beban domestik keluarga baru. Beberapa benda yang bisa pilih antara lain yakni vacuum cleaner, sapu, kain pel.
Jangan Mudah Tergoda dengan Harga Murah
Waspadai produk dengan harga tidak wajar seperti terlalu murah ataupun tidak sesuai dengan harga pasaran. Sebab, hal tersebut dapat menjadi salah satu indikasi produk yang ada kurang berkualitas maupun penipuan.
Inilah 3 tips yang bisa Anda terapkan untuk menghindari terjadinya refund. Pastikan Anda tidak tergesa-gesa saat membeli suatu barang. Pertimbangkan pilihan yang ada dan bandingkan dengan barang sejenisnya. Baca juga ketentuan refund yang ada sejelas-jelasnya.
Semoga dengan adanya informasi ini Anda dapat memahami bahwa refund artinya pengembalian dana yang terjadi akibat suatu hal dan atas dasar kesepakatan dua belah pihak.
Cara Mudah Dapat Modal Usaha
Khusus Sobat BFI yang tertarik untuk membuka usaha sendiri, BFI Finance menawarkan pinjaman modal usaha dengan proses mudah dan cepat!
Ajukan pinjaman modal usaha hanya di BFI Finance, klik tautan berikut untuk informasi selengkapnya.
Pencairan dana hingga 85% dari nilai kendaraan dan tenor hingga 4 tahun.
Pinjaman dana dengan proses cepat dan tenor maksimal hingga 24 bulan.
Jaminan Sertifikat Rumah
Bunga rendah mulai dari 0.9% dengan tenor panjang hingga 7 tahun.
Jangan sampai ketinggal berita terbaru seputar keuangan, bisnis, pinjaman, dan lainnya. Cek BFI Blog untuk artikel terbaru setiap minggunya!
Pernikahan adalah sesuatu yang sakral dan menjadi momen haru penuh bahagia. Sebagai tamu undangan, tentunya kita ingin memberikan ucapan selamat dan dukungan atas kebahagiaan kedua mempelai pengantin lewat kado pernikahan.
Kado pernikahan merupakan simbol doa, harapan, dan bentuk dukungan bagi kedua mempelai dalam menjalani kehidupan baru bersama pasangan. Selain itu, adanya pemberian hadiah turut menjaga tali silaturahmi antar kedua belah pihak dan mampu mempererat kedekatan yang ada.
Meskipun begitu, ada kalanya kita merasa kebingungan untuk memilih hadiah apa yang kiranya pas untuk dijadikan kado pernikahan. Nah, bagi Anda yang tengah berada di posisi ini, Anda tidak perlu khawatir karena Tim BFI Finance punya tips dan ide kado menarik yang bisa membantu Anda memilih hadiah yang tepat. Yuk, simak selengkapnya di artikel berikut!
7 Tips Memilih Kado Pernikahan
Sebelum membeli kado pernikahan, ada baiknya Anda mempertimbangkan beberapa hal berikut ini supaya Anda tidak salah pilih dalam memilih kado yang sesuai.
Pilih Kado Unik dan Anti Mainstream
Untuk menambah kesan yang berbeda dan tidak biasa, Anda bisa memilih kado pernikahan yang unik dan antimainstream. Namun, pastikan hadiah yang Anda pilih masih berkaitan dengan minat dan kepribadian kedua mempelai pengantin, ya!
Peralatan Makan dan Masak
Jika Anda mencari hadiah pernikahan yang bermanfaat dan bisa digunakan untuk kegiatan sehari-hari, pertimbangkan untuk membeli peralatan makan dan masak, seperti 1 set alat makan, gelas, toples, panci, dan lain sebagainya.
Hadiah tersebut dapat membantu pengantin baru untuk menekan pengeluaran rumah tangga dan melengkapi kebutuhan rumah tangga. Pasangan yang mendapatkan hadiah ini tentunya akan sangat berterima kasih pada Anda.
Pernikahan identik dengan tempat tinggal baru. Tidak ada salahnya untuk memberikan hadiah yang dapat mempercantik interior rumah. Anda bisa memilih jam dinding, tanaman hias, lukisan, vas bunga, daan ragam jenis dekorasi lainnya.
Album Foto Kenangan
Foto album bisa menjadi ide kado pernikahan berikutnya yang tidak kalah memukau, terutama jika kado tersebut dipersembahkan untuk mereka yang memiliki kedekatan secara emosional. Seperti saudara kandung, sahabat, dan lainnya.
Baca Juga: Siap Berumah Tangga? Intip Estimasi Biaya Lamaran Sederhana Berikut
Perabotan rumah tangga atau furniture bisa menjadi ide berikutnya yang Anda pilih. Pasalnya, pasangan yang baru menikah umumnya belum memiliki banyak furniture untuk tempat tinggal mereka yang baru.
Selain memberikan logam mulia dan emas, Anda juga bisa mempertimbangkan untuk memberikan aset investasi berupa saham, obligasi, surat tanah, dan lain sebagainya. Selain berkesan, aset tersebut akan sangat berguna karena memiliki nilai yang cukup besar.
Sobat BFI, demikian pembahasan terkait kado pernikahan. Semoga dengan adanya artikel ini Anda bisa memilih hadiah terbaik untuk diberikan kepada kerabat, teman, saudara, atau siapapun itu yang Anda pedulikan. Pilihlah hadiah yang mampu menciptakan kenangan dan dapat digunakan untuk jangka waktu lama.
Jika Anda dan pasangan berencana untuk melangsungkan hubungan ke jenjang yang lebih serius namun terhalang oleh modal pernikahan, BFI Finance siap sedia membantu Anda!
Anda bisa mengajukan pinjaman dana dengan jaminan BPKB mobil untuk biaya pernikahan yang lebih besar. Dapatkan berbagai keuntungan serta kemudahan dengan mengajukan pinjaman dana ke BFI Finance. Untuk informasi selengkapnya klik tautan berikut ini, ya!
Dapatkan dana pencairan hingga 85% dari nilai kendaraan dan tenor hingga 4 tahun.
Dapatkan pinjaman dengan proses cepat dan tenor maksimal hingga 24 bulan.
Jaminan Sertifikat Rumah
Bunga rendah mulai dari 0.9% per bulan dan tenor panjang hingga 7 tahun.
BFI Finance adalah perusahaan pembiayaan terpercaya sejak tahun 1982. BFI Finance telah melayani dan membantu ribuan masyarakat untuk mewujudkan berbagai kebutuhan dan impian. Terverifikasi oleh OJK (Otoritas Jasa Keuangan), pinjam di BFI prosesnya cepat, aman, dan mudah. Tunggu apa lagi? Yuk, dapatkan pinjaman dana hingga 85% dari nilai aset yang dijaminkan jika persyaratan lengkap!
Temukan artikel bermanfaat lainnya hanya di BFI Blog. Artikel terbaru setiap Senin-Jumat!
Melansir Makeuseof, desain CPU sangat kompleks dan sangat bervariasi antara perusahaan dan model. Namun terlepas dari semua perbedaan arsitektural, Kerja CPU adalah melewati empat langkah utama setiap kali mereka memproses instruksi: mengambil, mendekode, mengeksekusi, dan memberi menulis balik.
Di sini, inti CPU mengambil instruksi yang menunggunya, biasanya dari semacam memori. Ini bisa termasuk RAM, tetapi instruksi biasanya sudah menunggu inti di dalam cache CPU di inti CPU modern. Prosesor memiliki area yang disebut penghitung program, yang pada dasarnya bertindak sebagai penanda, memberi tahu prosesor di mana instruksi terakhir berakhir, dan instruksi berikutnya dimulai.
Mendekode atau membaca sandi dalam CPU adalah proses memecahkan kode. Setelah mengambil instruksi langsung, ia melanjutkan untuk memecahkan kode itu. Instruksi sering kali melibatkan beberapa area inti CPU—seperti aritmatika—dan inti CPU perlu mengetahui hal ini.
Setiap bagian memiliki sesuatu yang disebut opcode yang memberi tahu inti CPU apa yang harus dilakukan dengan informasi yang mengikutinya. Setelah inti CPU mengetahui semua ini, berbagai area inti itu sendiri dapat mulai bekerja.
Langkah eksekusi pada CPU adalah saat CPU mengetahui apa yang perlu dilakukan, dan benar-benar melanjutkan dan melakukannya. Apa yang terjadi di sini bervariasi tergantung pada area inti CPU yang digunakan dan informasi yang dimasukkan.
Misalnya, CPU dapat melakukan aritmatika di dalam ALU, atau Unit Logika Aritmatika. Unit ini dapat terhubung ke input dan output yang berbeda untuk menghitung angka dan mendapatkan hasil yang diinginkan.
Langkah terakhir, yang disebut writeback, hanya menempatkan hasil dari apa yang telah dikerjakan kembali ke dalam memori. Ke mana tepatnya keluaran itu pergi tergantung pada kebutuhan aplikasi yang sedang berjalan, tetapi sering kali tetap berada di register prosesor untuk akses cepat karena instruksi berikut sering menggunakannya.
Dalam dunia astrologi, pemahaman tentang elemen-elemen zodiak adalah langkah penting untuk memahami karakteristik dan kepribadian seseorang. Elemen-elemen ini membantu kita memahami cara individu berinteraksi dengan dunia, merasakan emosi, dan mengekspresikan diri. Ada empat elemen zodiak utama: Air, Tanah, Api, dan Udara. Dalam artikel ini, kita akan menggali masing-masing elemen zodiak dan membahas kecocokan zodiak berdasarkan elemen tersebut. Jadi, apakah Anda adalah seorang pemikir bebas dari elemen Udara, atau seorang pribadi yang tulus dan praktis dari elemen Tanah? Mari kita temukan!
Baca Juga: Mengenal Zodiak, dan Bagaimana 12 Zodiak Berelasi dengan Pasangannya. Kalau Kamu Termasuk Tipe yang Mana?
Elemen Air dalam zodiak meliputi tiga tanda: Gemini, Libra, dan Aquarius. Orang yang terkait dengan elemen ini cenderung berpikir secara abstrak, intelektual, dan berorientasi pada ide. Mereka suka berkomunikasi dan sering menjadi penghubung sosial dalam kelompok mereka. Orang-orang Air cenderung kreatif, suka berbagi ide, dan memiliki kemampuan komunikasi yang kuat.
Sifat Air: Orang yang berasal dari elemen Air cenderung fleksibel dalam berpikir, suka bertukar gagasan, dan terbuka terhadap perubahan. Mereka memiliki kecenderungan untuk memproses informasi secara logis dan rasional. Keinginan untuk menjelajahi ide-ide baru dan berpikir 'di luar kotak' adalah salah satu ciri khas dari elemen ini.
Elemen Tanah mencakup tiga tanda: Taurus, Virgo, dan Capricorn. Individu yang terkait dengan elemen ini memiliki sifat praktis, konservatif, dan terfokus pada hal-hal nyata. Mereka cenderung memiliki ketelitian yang tinggi dan menghargai stabilitas dalam kehidupan. Orang-orang Tanah adalah pekerja keras yang memiliki kecenderungan untuk mencapai tujuan mereka dengan metode yang teliti dan terencana.
Sifat Tanah: Orang-orang yang berasal dari elemen Tanah adalah individu yang bertanggung jawab dan cenderung memiliki nilai-nilai yang kuat terkait dengan keamanan finansial dan stabilitas. Mereka memahami nilai-nilai materi dan cenderung memperhatikan detail.
Elemen Api terdiri dari tiga tanda: Aries, Leo, dan Sagittarius. Individu yang terkait dengan elemen ini penuh gairah, energik, dan penuh semangat. Mereka cenderung berani, kompetitif, dan memiliki dorongan yang kuat untuk mencapai tujuan. Orang-orang Api suka menjadi pusat perhatian dan seringkali memiliki karisma yang kuat.
Sifat Api: Orang-orang yang berasal dari elemen Api adalah penuh semangat dan percaya diri. Mereka memiliki hasrat untuk mencapai sesuatu dan tidak takut untuk mengambil risiko. Mereka juga memiliki sifat kepemimpinan dan suka berada di pusat perhatian.
Elemen Udara meliputi tiga tanda: Gemini, Libra, dan Aquarius (Ya, dua tanda Air yang sama dengan sebelumnya). Orang-orang yang terkait dengan elemen ini cenderung rasional, objektif, dan suka berpikir secara logis. Mereka sering menjadi pemikir bebas dan menyukai diskusi intelektual. Orang-orang Udara memiliki kemampuan untuk memahami berbagai sudut pandang dan sering menjadi penengah dalam situasi konflik.
Sifat Udara: Individu yang berasal dari elemen Udara adalah berpikir kritis dan suka mempertanyakan hal-hal. Mereka memiliki kecenderungan untuk menjadi objektif dalam pengambilan keputusan dan tidak mudah terbawa emosi. Mereka juga suka berbagi gagasan dan bersifat sosial.
Baca Juga: Membongkar Misteri Daya Tarik: Apa yang Membuat Orang Terpesona oleh Zodiak Ini?
Cara Melakukan Refund
Cara melakukan refund dapat Anda lakukan dengan mudah sesuai dengan syarat dan ketentuan yang disediakan oleh pihak penjual. Meskipun demikian, tidak ada salahnya jika Anda melakukan beberapa persiapan berikut ini agar proses refund dapat berjalan sebagaimana mestinya.
Image Source: Freepik/timeimage
Hardware performance counter
Many modern architectures (including embedded ones) often include hardware performance counters (HPC), which enables low-level (instruction-level) collection, benchmarking, debugging or analysis of running software metrics.[81][82] HPC may also be used to discover and analyze unusual or suspicious activity of the software, such as return-oriented programming (ROP) or sigreturn-oriented programming (SROP) exploits etc.[83] This is usually done by software-security teams to assess and find malicious binary programs.[84]
Many major vendors (such as IBM, Intel, AMD, and Arm) provide software interfaces (usually written in C/C++) that can be used to collect data from the CPU's registers in order to get metrics.[85] Operating system vendors also provide software like perf (Linux) to record, benchmark, or trace CPU events running kernels and applications.
Hardware counters provide a low-overhead method for collecting comprehensive performance metrics related to a CPU's core elements (functional units, caches, main memory, etc.) – a significant advantage over software profilers.[86] Additionally, they generally eliminate the need to modify the underlying source code of a program.[87][88] Because hardware designs differ between architectures, the specific types and interpretations of hardware counters will also change.
Most modern CPUs have privileged modes to support operating systems and virtualization.
Cloud computing can use virtualization to provide virtual central processing units[89] (vCPUs) for separate users.[90]
A host is the virtual equivalent of a physical machine, on which a virtual system is operating.[91] When there are several physical machines operating in tandem and managed as a whole, the grouped computing and memory resources form a cluster. In some systems, it is possible to dynamically add and remove from a cluster. Resources available at a host and cluster level can be partitioned into resources pools with fine granularity.
The performance or speed of a processor depends on, among many other factors, the clock rate (generally given in multiples of hertz) and the instructions per clock (IPC), which together are the factors for the instructions per second (IPS) that the CPU can perform.[92] Many reported IPS values have represented "peak" execution rates on artificial instruction sequences with few branches, whereas realistic workloads consist of a mix of instructions and applications, some of which take longer to execute than others. The performance of the memory hierarchy also greatly affects processor performance, an issue barely considered in IPS calculations. Because of these problems, various standardized tests, often called "benchmarks" for this purpose— such as SPECint—have been developed to attempt to measure the real effective performance in commonly used applications.
Processing performance of computers is increased by using multi-core processors, which essentially is plugging two or more individual processors (called cores in this sense) into one integrated circuit.[93] Ideally, a dual core processor would be nearly twice as powerful as a single core processor. In practice, the performance gain is far smaller, only about 50%, due to imperfect software algorithms and implementation.[94] Increasing the number of cores in a processor (i.e. dual-core, quad-core, etc.) increases the workload that can be handled. This means that the processor can now handle numerous asynchronous events, interrupts, etc. which can take a toll on the CPU when overwhelmed. These cores can be thought of as different floors in a processing plant, with each floor handling a different task. Sometimes, these cores will handle the same tasks as cores adjacent to them if a single core is not enough to handle the information. Multi-core CPUs enhance a computer's ability to run several tasks simultaneously by providing additional processing power. However, the increase in speed is not directly proportional to the number of cores added. This is because the cores need to interact through specific channels, and this inter-core communication consumes a portion of the available processing speed.[95]
Due to specific capabilities of modern CPUs, such as simultaneous multithreading and uncore, which involve sharing of actual CPU resources while aiming at increased utilization, monitoring performance levels and hardware use gradually became a more complex task.[96] As a response, some CPUs implement additional hardware logic that monitors actual use of various parts of a CPU and provides various counters accessible to software; an example is Intel's Performance Counter Monitor technology.[9]
Full Refund (Pengembalian Dana 100%)
Full refund adalah jenis refund yang menawarkan pengembalian uang secara 100% sesuai dengan jumlah nominal transaksi yang Anda keluarkan sebelumnya. Full refund seringkali digunakan di marketplace seperti Tokopedia atau Shopee.
Nantinya, dana yang dikembalikan akan dikirim melalui alamat pengembalian yang Anda pilih, seperti rekening bank, e-wallet, dan lain sebagainya. Dengan catatan jika Anda mengajukan refund di marketplace pastikan Anda belum mengklik tombol konfirmasi pembelian (barang sudah diterima).
Large-scale integration CPUs
Lee Boysel published influential articles, including a 1967 "manifesto", which described how to build the equivalent of a 32-bit mainframe computer from a relatively small number of large-scale integration circuits (LSI).[49][50] The only way to build LSI chips, which are chips with a hundred or more gates, was to build them using a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) semiconductor manufacturing process (either PMOS logic, NMOS logic, or CMOS logic). However, some companies continued to build processors out of bipolar transistor–transistor logic (TTL) chips because bipolar junction transistors were faster than MOS chips up until the 1970s (a few companies such as Datapoint continued to build processors out of TTL chips until the early 1980s).[50] In the 1960s, MOS ICs were slower and initially considered useful only in applications that required low power.[51][52] Following the development of silicon-gate MOS technology by Federico Faggin at Fairchild Semiconductor in 1968, MOS ICs largely replaced bipolar TTL as the standard chip technology in the early 1970s.[53]
As the microelectronic technology advanced, an increasing number of transistors were placed on ICs, decreasing the number of individual ICs needed for a complete CPU. MSI and LSI ICs increased transistor counts to hundreds, and then thousands. By 1968, the number of ICs required to build a complete CPU had been reduced to 24 ICs of eight different types, with each IC containing roughly 1000 MOSFETs.[54] In stark contrast with its SSI and MSI predecessors, the first LSI implementation of the PDP-11 contained a CPU composed of only four LSI integrated circuits.[55]
Since microprocessors were first introduced they have almost completely overtaken all other central processing unit implementation methods. The first commercially available microprocessor, made in 1971, was the Intel 4004, and the first widely used microprocessor, made in 1974, was the Intel 8080. Mainframe and minicomputer manufacturers of the time launched proprietary IC development programs to upgrade their older computer architectures, and eventually produced instruction set compatible microprocessors that were backward-compatible with their older hardware and software. Combined with the advent and eventual success of the ubiquitous personal computer, the term CPU is now applied almost exclusively[a] to microprocessors. Several CPUs (denoted cores) can be combined in a single processing chip.[56]
Previous generations of CPUs were implemented as discrete components and numerous small integrated circuits (ICs) on one or more circuit boards.[57] Microprocessors, on the other hand, are CPUs manufactured on a very small number of ICs; usually just one.[58] The overall smaller CPU size, as a result of being implemented on a single die, means faster switching time because of physical factors like decreased gate parasitic capacitance.[59][60] This has allowed synchronous microprocessors to have clock rates ranging from tens of megahertz to several gigahertz. Additionally, the ability to construct exceedingly small transistors on an IC has increased the complexity and number of transistors in a single CPU many fold. This widely observed trend is described by Moore's law, which had proven to be a fairly accurate predictor of the growth of CPU (and other IC) complexity until 2016.[61][62]
While the complexity, size, construction and general form of CPUs have changed enormously since 1950,[63] the basic design and function has not changed much at all. Almost all common CPUs today can be very accurately described as von Neumann stored-program machines.[64][b] As Moore's law no longer holds, concerns have arisen about the limits of integrated circuit transistor technology. Extreme miniaturization of electronic gates is causing the effects of phenomena like electromigration and subthreshold leakage to become much more significant.[66][67] These newer concerns are among the many factors causing researchers to investigate new methods of computing such as the quantum computer, as well as to expand the use of parallelism and other methods that extend the usefulness of the classical von Neumann model.
The fundamental operation of most CPUs, regardless of the physical form they take, is to execute a sequence of stored instructions that is called a program. The instructions to be executed are kept in some kind of computer memory. Nearly all CPUs follow the fetch, decode and execute steps in their operation, which are collectively known as the instruction cycle.
After the execution of an instruction, the entire process repeats, with the next instruction cycle normally fetching the next-in-sequence instruction because of the incremented value in the program counter. If a jump instruction was executed, the program counter will be modified to contain the address of the instruction that was jumped to and program execution continues normally. In more complex CPUs, multiple instructions can be fetched, decoded and executed simultaneously. This section describes what is generally referred to as the "classic RISC pipeline", which is quite common among the simple CPUs used in many electronic devices (often called microcontrollers). It largely ignores the important role of CPU cache, and therefore the access stage of the pipeline.
Some instructions manipulate the program counter rather than producing result data directly; such instructions are generally called "jumps" and facilitate program behavior like loops, conditional program execution (through the use of a conditional jump), and existence of functions.[c] In some processors, some other instructions change the state of bits in a "flags" register. These flags can be used to influence how a program behaves, since they often indicate the outcome of various operations. For example, in such processors a "compare" instruction evaluates two values and sets or clears bits in the flags register to indicate which one is greater or whether they are equal; one of these flags could then be used by a later jump instruction to determine program flow.
Fetch involves retrieving an instruction (which is represented by a number or sequence of numbers) from program memory. The instruction's location (address) in program memory is determined by the program counter (PC; called the "instruction pointer" in Intel x86 microprocessors), which stores a number that identifies the address of the next instruction to be fetched. After an instruction is fetched, the PC is incremented by the length of the instruction so that it will contain the address of the next instruction in the sequence.[d] Often, the instruction to be fetched must be retrieved from relatively slow memory, causing the CPU to stall while waiting for the instruction to be returned. This issue is largely addressed in modern processors by caches and pipeline architectures (see below).
The instruction that the CPU fetches from memory determines what the CPU will do. In the decode step, performed by binary decoder circuitry known as the instruction decoder, the instruction is converted into signals that control other parts of the CPU.
The way in which the instruction is interpreted is defined by the CPU's instruction set architecture (ISA).[e] Often, one group of bits (that is, a "field") within the instruction, called the opcode, indicates which operation is to be performed, while the remaining fields usually provide supplemental information required for the operation, such as the operands. Those operands may be specified as a constant value (called an immediate value), or as the location of a value that may be a processor register or a memory address, as determined by some addressing mode.
In some CPU designs, the instruction decoder is implemented as a hardwired, unchangeable binary decoder circuit. In others, a microprogram is used to translate instructions into sets of CPU configuration signals that are applied sequentially over multiple clock pulses. In some cases the memory that stores the microprogram is rewritable, making it possible to change the way in which the CPU decodes instructions.
After the fetch and decode steps, the execute step is performed. Depending on the CPU architecture, this may consist of a single action or a sequence of actions. During each action, control signals electrically enable or disable various parts of the CPU so they can perform all or part of the desired operation. The action is then completed, typically in response to a clock pulse. Very often the results are written to an internal CPU register for quick access by subsequent instructions. In other cases results may be written to slower, but less expensive and higher capacity main memory.
For example, if an instruction that performs addition is to be executed, registers containing operands (numbers to be summed) are activated, as are the parts of the arithmetic logic unit (ALU) that perform addition. When the clock pulse occurs, the operands flow from the source registers into the ALU, and the sum appears at its output. On subsequent clock pulses, other components are enabled (and disabled) to move the output (the sum of the operation) to storage (e.g., a register or memory). If the resulting sum is too large (i.e., it is larger than the ALU's output word size), an arithmetic overflow flag will be set, influencing the next operation.